How to use the label parser
This tutorial shows how to use the label parser to easily access labels' content.
Setup
%pip install kili
from kili.client import Kili
kili = Kili()
Kili labels
In Kili SDK, a label is a dictionary that follows a json structure as described in the documentation:
my_label = kili.labels(project_id="my_project_id", output_format='dict')[0]
print(my_label)
{
"id": "abc123",
"author": {"email": "john.doe@kili-techonology.com", "id": "123456"},
"createdAt": "2020-02-20T14:00:00.000Z",
"labelType": "DEFAULT",
"secondsToLabel": 10,
"jsonResponse": {},
... // many other possible fields!
}
The jsonResponse field is the one that contains the actual label data, that is the data that the annotator has entered in the interface (the bounding boxes, polygons, text, etc.).
Is it however quite difficult to extract the label data from the jsonResponse field, as it is a nested dictionary. This is why we have developed a label parser that allows you to extract the label data in a more convenient way.
Parsed Label integration to kili.labels()
The kili.labels() method has an output_format argument that enables automatic label parsing.
my_label = kili.labels(project_id="my_project_id", output_format='parsed_label')[0]
# example of how to access the category name of the first label
my_label.jobs["MY_JOB_NAME"].category.name
Instead of:
my_label = kili.labels(project_id="my_project_id", output_format='dict')[0]
# example of how to access the category name of the first label
my_label["jsonResponse"]["jobs"]["MY_JOB_NAME"]["categories"][0]["name"]
As you can see, the parsed label is much easier to use than the raw label, and helps you develop your own scripts faster using your IDE auto-completion, type checking, etc.
ParsedLabel class
The ParsedLabel class represents a Kili label with a parsed json response.
As we have seen earlier, the kili.labels(..., output_format='parsed_label') will automatically return a list of ParsedLabel objects, but you can also create a ParsedLabel object from a raw dict label.
from kili.utils.labels.parsing import ParsedLabel
This class directly inherits from dict, and thus behaves like a dictionary.
print(ParsedLabel.__bases__[0])
<class 'dict'>
Converting a label to a ParsedLabel is as simple as:
my_label = {
"author": {"email": "first.last@kili-technology.com", "id": "123456"},
"id": "clh0fsi9u0tli0j666l4sfhpz",
"jsonResponse": {"CLASSIFICATION_JOB": {"categories": [{"confidence": 100, "name": "A"}]}},
"labelType": "DEFAULT",
"secondsToLabel": 5,
}
my_parsed_label = ParsedLabel(my_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(my_parsed_label["author"]["email"])
first.last@kili-technology.com
In a parsed label, the jsonResponse dict key is not accessible anymore, since it is parsed and transformed into a .jobs object:
try:
my_parsed_label["jsonResponse"]
except KeyError as err:
print(f"The key {err} is not accessible anymore.")
The key 'jsonResponse' is not accessible anymore.
.jobs attribute
The .jobs attribute of a ParsedLabel class is a dictionary-like object that contains the json response data of a parsed label.
The keys are the names of the jobs, and the values are the parsed job responses.
Let's illustrate this with the previous label.
print(list(my_parsed_label.jobs.keys()))
['CLASSIFICATION_JOB']
The values are ParsedJob objects, which are also dictionary-like objects that contain the job response data.
The available data attributes are specific to the job interface described in the ontology (also called the json interface).
print(my_parsed_label.jobs["CLASSIFICATION_JOB"])
{'categories': [{'name': 'A', 'confidence': 100}]}
For example, for a classification job, the available data attributes are categories or category, and a category object can have a name and a confidence attribute.
print(my_parsed_label.jobs["CLASSIFICATION_JOB"].categories[0].name)
A
Autocomplete
The ParsedLabel class enables your IDE to explore the possible attributes during development:
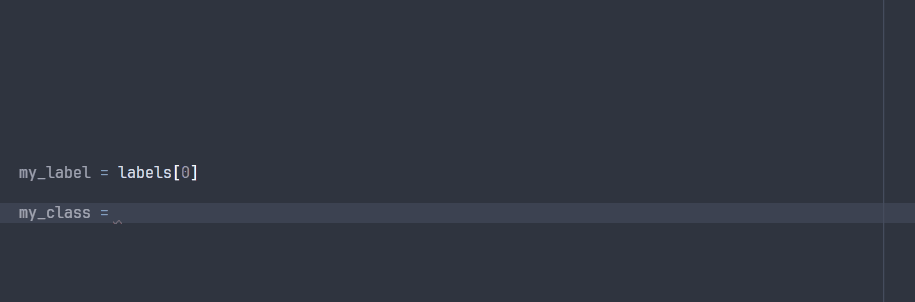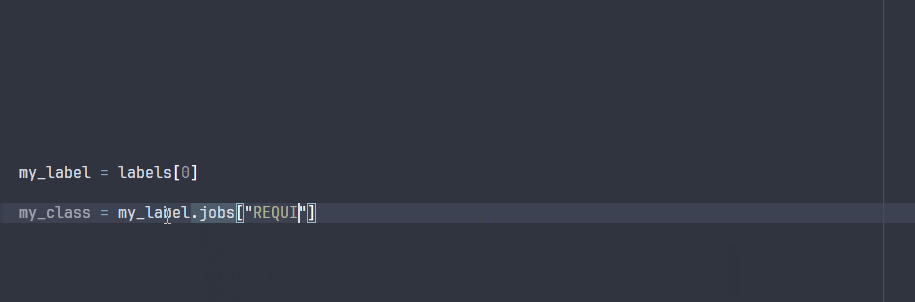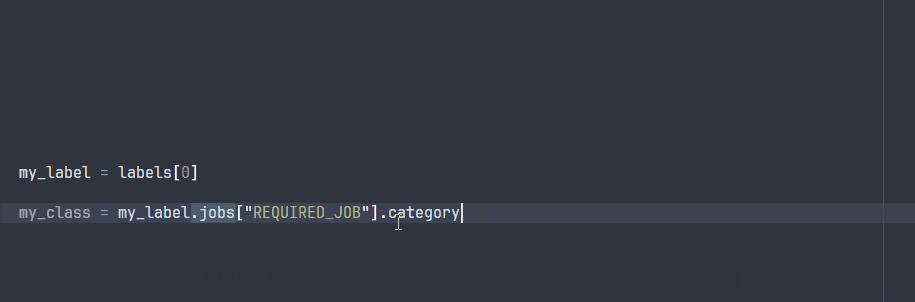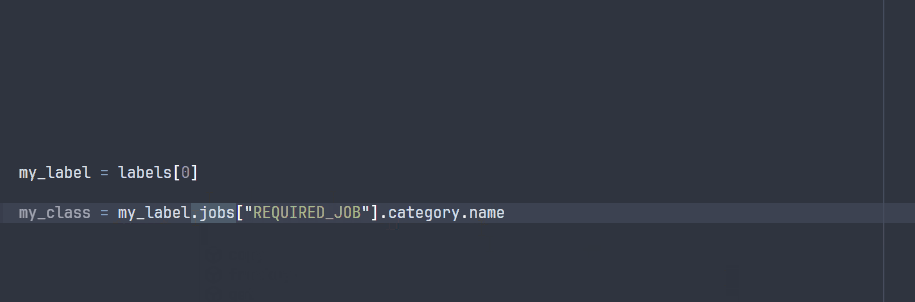
Note that some attributes will not be avaible at runtime, since they are specific to the project ontology that will only be known at runtime.
Get the json response from a parsed label
If you need to get the json response from a parsed label, you can use the .json_response attribute:
print(type(my_parsed_label.json_response))
<class 'dict'>
print(my_parsed_label.json_response)
{'CLASSIFICATION_JOB': {'categories': [{'name': 'A', 'confidence': 100}]}}
Convert ParsedLabel to Python dict
A ParsedLabel is a custom class and is not serializable by default. However, it is possible to convert it to a Python dict using the to_dict method:
print(type(my_parsed_label))
<class 'kili.utils.labels.parsing.ParsedLabel'>
label_as_dict = my_parsed_label.to_dict()
print(type(label_as_dict))
<class 'dict'>
print(label_as_dict)
{'author': {'email': 'first.last@kili-technology.com', 'id': '123456'}, 'id': 'clh0fsi9u0tli0j666l4sfhpz', 'labelType': 'DEFAULT', 'secondsToLabel': 5, 'jsonResponse': {'CLASSIFICATION_JOB': {'categories': [{'name': 'A', 'confidence': 100}]}}}
Task specific attributes
Classification jobs
We define a json interface for two classification jobs:
- a single-class classification job, with name
SINGLE_CLASS_JOBand three categoriesA,BandC - a multi-class classification job, with name
MULTI_CLASS_JOBand three categoriesD,EandF.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"SINGLE_CLASS_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": [], "name": "A"},
"B": {"children": [], "name": "B"},
"C": {"children": [], "name": "C"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Class",
"mlTask": "CLASSIFICATION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
},
"MULTI_CLASS_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"D": {"children": [], "name": "D"},
"E": {"children": [], "name": "E"},
"F": {"children": [], "name": "F"},
},
"input": "checkbox",
},
"instruction": "Class",
"mlTask": "CLASSIFICATION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
},
}
}
For this tutorial, we will work with already existing labels.
Note that those labels could have been downloaded from a real Kili project using the kili.labels() method.
To learn more about the json response format for classification jobs, please refer to the documentation.
json_responses = [
{
"SINGLE_CLASS_JOB": {"categories": [{"confidence": 75, "name": "A"}]},
"MULTI_CLASS_JOB": {
"categories": [{"confidence": 1, "name": "D"}, {"confidence": 1, "name": "E"}]
},
},
{
"SINGLE_CLASS_JOB": {"categories": [{"confidence": 50, "name": "B"}]},
"MULTI_CLASS_JOB": {
"categories": [{"confidence": 2, "name": "E"}, {"confidence": 2, "name": "F"}]
},
},
{
"SINGLE_CLASS_JOB": {"categories": [{"confidence": 25, "name": "C"}]},
"MULTI_CLASS_JOB": {
"categories": [{"confidence": 3, "name": "F"}, {"confidence": 3, "name": "D"}]
},
},
]
labels = [
ParsedLabel({"jsonResponse": label}, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
for label in json_responses
]
print(labels[0].jobs["SINGLE_CLASS_JOB"])
{'categories': [{'name': 'A', 'confidence': 75}]}
print(labels[0].jobs["SINGLE_CLASS_JOB"].categories)
[{'name': 'A', 'confidence': 75}]
print(labels[0].jobs["SINGLE_CLASS_JOB"].categories[0].name)
A
Since SINGLE_CLASS_JOB is a single-category classification job, the .category attribute is available, and is an alias for .categories[0]:
print(labels[0].jobs["SINGLE_CLASS_JOB"].category.name)
print(labels[0].jobs["SINGLE_CLASS_JOB"].category.confidence)
A
75
The .category attribute is forbidden for multi-category classification jobs:
try:
print(labels[0].jobs["MULTI_CLASS_JOB"].category.name)
except Exception as err:
print("Error: ", err)
Error: The attribute 'category' is not compatible with the job.
It is also possible to iterate over the job names:
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
print(f"\nLabel {i}")
for job_name, job_data in label.jobs.items():
print("job_name: ", job_name)
for category in job_data.categories:
print("category: ", category.name, category.confidence)
Label 0
job_name: SINGLE_CLASS_JOB
category: A 75
job_name: MULTI_CLASS_JOB
category: D 1
category: E 1
Label 1
job_name: SINGLE_CLASS_JOB
category: B 50
job_name: MULTI_CLASS_JOB
category: E 2
category: F 2
Label 2
job_name: SINGLE_CLASS_JOB
category: C 25
job_name: MULTI_CLASS_JOB
category: F 3
category: D 3
Transcription jobs
For a transcription job, you can access the label data through the .text attribute:
json_interface = {
"jobs": {"TRANSCRIPTION_JOB": {"mlTask": "TRANSCRIPTION", "required": 1, "isChild": False}}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {"TRANSCRIPTION_JOB": {"text": "This is a transcription annotation..."}}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="TEXT")
print(label.jobs["TRANSCRIPTION_JOB"].text)
This is a transcription annotation...
Object detection jobs
Standard object detection job
For standard object detection jobs, a parsed label has an .annotations attribute:
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"tools": ["rectangle"],
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
"content": {"categories": {"A": {}, "B": {}}, "input": "radio"},
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
{"x": 0.54, "y": 0.52},
{"x": 0.54, "y": 0.33},
{"x": 0.70, "y": 0.33},
{"x": 0.70, "y": 0.52},
]
}
],
"categories": [{"name": "B"}],
"mid": "20230315142306286-25528",
"type": "rectangle",
}
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].category.name)
B
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].type)
rectangle
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].bounding_poly)
[{'normalizedVertices': [{'x': 0.54, 'y': 0.52}, {'x': 0.54, 'y': 0.33}, {'x': 0.7, 'y': 0.33}, {'x': 0.7, 'y': 0.52}]}]
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].bounding_poly[0].normalized_vertices)
[{'x': 0.54, 'y': 0.52}, {'x': 0.54, 'y': 0.33}, {'x': 0.7, 'y': 0.33}, {'x': 0.7, 'y': 0.52}]
The .bounding_poly_annotations attribute is equivalent to .annotations:
print(
label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations
== label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].bounding_poly_annotations
)
True
Point detection jobs
The point coordinates of a point detection label are accessible through the .point attribute:
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": [], "color": "#472CED", "name": "A"},
"B": {"children": [], "name": "B", "color": "#5CE7B7"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Class",
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"required": 1,
"tools": ["marker"],
"isChild": False,
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"point": {"x": 0.10, "y": 0.20},
"categories": [{"name": "A"}],
"mid": "20230323113855529-11197",
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"point": {"x": 0.30, "y": 0.40},
"categories": [{"name": "B"}],
"mid": "20230323113857016-51829",
"type": "marker",
},
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[1].type)
marker
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[1].point)
{'x': 0.3, 'y': 0.4}
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[1].category.name)
B
Line detection jobs
A polyline parsed label has a .polyline attribute.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": [], "color": "#472CED", "name": "A"},
"B": {"children": [], "name": "B", "color": "#5CE7B7"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Job name",
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"required": 1,
"tools": ["polyline"],
"isChild": False,
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"polyline": [{"x": 0.59, "y": 0.40}, {"x": 0.25, "y": 0.30}],
"categories": [{"name": "A"}],
"mid": "20230428163557647-23000",
"type": "polyline",
},
{
"children": {},
"polyline": [{"x": 0.70, "y": 0.50}, {"x": 0.40, "y": 0.70}],
"categories": [{"name": "B"}],
"mid": "20230428163606237-86143",
"type": "polyline",
},
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(len(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations))
2
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].category.name)
A
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].polyline)
[{'x': 0.59, 'y': 0.4}, {'x': 0.25, 'y': 0.3}]
Pose estimation jobs
A pose estimation parsed label annotation has a .points attribute that returns the list of points that make up the annotation.
Read more about pose estimation json response in the documentation.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"JOB_0": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"HEAD": {
"children": [],
"name": "Head",
"color": "#733AFB",
"points": [
{"code": "RIGHT_EARBASE", "name": "Right earbase"},
{"code": "RIGHT_EYE", "name": "Right eye"},
{"code": "NOSE", "name": "Nose"},
{"code": "LEFT_EYE", "name": "Left eye"},
{"code": "LEFT_EARBASE", "name": "Left earbase"},
],
},
"BODY": {
"children": [],
"name": "Body",
"color": "#3CD876",
"points": [
{"code": "THROAT", "name": "Throat"},
{"code": "WITHERS", "name": "Withers"},
{"code": "TAILBASE", "name": "Tailbase"},
],
},
"FRONT_RIGHT_LEG": {
"children": [],
"name": "Front right leg",
"color": "#3BCADB",
"points": [
{"code": "PAW", "name": "Paw"},
{"code": "KNEE", "name": "Knee"},
{"code": "ELBOW", "name": "Elbow"},
],
},
"FRONT_LEFT_LEG": {
"children": [],
"name": "Front left leg",
"color": "#199CFC",
"points": [
{"code": "PAW", "name": "Paw"},
{"code": "KNEE", "name": "Knee"},
{"code": "ELBOW", "name": "Elbow"},
],
},
"BACK_RIGHT_LEG": {
"children": [],
"name": "Back right leg",
"color": "#FA484A",
"points": [
{"code": "PAW", "name": "Paw"},
{"code": "KNEE", "name": "Knee"},
{"code": "ELBOW", "name": "Elbow"},
],
},
"BACK_LEFT_LEG": {
"children": [],
"name": "Back left leg",
"color": "#ECB82A",
"points": [
{"code": "PAW", "name": "Paw"},
{"code": "KNEE", "name": "Knee"},
{"code": "ELBOW", "name": "Elbow"},
],
},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Body parts from the animal point of view",
"isChild": False,
"tools": ["pose"],
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"models": {},
"isVisible": True,
"required": 0,
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"JOB_0": {
"annotations": [
{
"categories": [{"name": "HEAD"}],
"children": {},
"mid": "20230220175803297-40094",
"points": [
{
"children": {},
"code": "RIGHT_EARBASE",
"mid": "20230220170039711-76095",
"point": {"x": 0.350897302238901, "y": 0.18537832978498114},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "RIGHT_EYE",
"mid": "20230220170039711-75233",
"point": {"x": 0.3581081932428414, "y": 0.2305347416594279},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "NOSE",
"mid": "20230220170039711-59132",
"point": {"x": 0.38815357242592613, "y": 0.32807259130823285},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "LEFT_EYE",
"mid": "20230220170039711-27852",
"point": {"x": 0.4386476019456967, "y": 0.23889914422760516},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "LEFT_EARBASE",
"mid": "20230220170039711-40802",
"point": {"x": 0.46187314422288966, "y": 0.1875659030559057},
"type": "marker",
},
],
"type": "pose",
},
{
"categories": [{"name": "BODY"}],
"children": {},
"mid": "20230220175812521-86245",
"points": [
{
"children": {},
"code": "THROAT",
"mid": "20230220170039712-55565",
"point": {"x": 0.41045627160921705, "y": 0.3819115257598137},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "WITHERS",
"mid": "20230220170039712-92408",
"point": {"x": 0.4818714352479842, "y": 0.2536057346999746},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "TAILBASE",
"mid": "20230220170039712-18390",
"point": {"x": 0.6107470753777133, "y": 0.17341461528757518},
"type": "marker",
},
],
"type": "pose",
},
{
"categories": [{"name": "FRONT_RIGHT_LEG"}],
"children": {},
"mid": "20230220175821453-77849",
"points": [
{
"children": {},
"code": "PAW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-77846",
"point": {"x": 0.3776217136143816, "y": 0.9050043662345423},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "KNEE",
"mid": "20230220170039712-53563",
"point": {"x": 0.4014267681606373, "y": 0.7026760034094114},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "ELBOW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-78929",
"point": {"x": 0.3907555368123158, "y": 0.5151521549373389},
"type": "marker",
},
],
"type": "pose",
},
{
"categories": [{"name": "FRONT_LEFT_LEG"}],
"children": {},
"mid": "20230220175828920-37602",
"points": [
{
"children": {},
"code": "PAW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-72948",
"point": {"x": 0.46873761205005, "y": 0.9148740424699144},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "KNEE",
"mid": "20230220170039712-67331",
"point": {"x": 0.4695584759999209, "y": 0.703909712938833},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "ELBOW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-86687",
"point": {"x": 0.4958261223957892, "y": 0.541060055055191},
"type": "marker",
},
],
"type": "pose",
},
{
"categories": [{"name": "BACK_RIGHT_LEG"}],
"children": {},
"mid": "20230220175834605-4761",
"points": [
{
"children": {},
"code": "PAW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-95942",
"point": {"x": 0.5303024082903665, "y": 0.7470895464685865},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "KNEE",
"mid": "20230220170039712-89543",
"point": {"x": 0.5623755076892811, "y": 0.5105044952809976},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "ELBOW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-61950",
"point": {"x": 0.5359355740081666, "y": 0.4003228503073476},
"type": "marker",
},
],
"type": "pose",
},
{
"categories": [{"name": "BACK_LEFT_LEG"}],
"children": {},
"mid": "20230220175849088-95977",
"points": [
{
"children": {},
"code": "PAW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-40305",
"point": {"x": 0.6741443182503564, "y": 0.7362865546532311},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "KNEE",
"mid": "20230220170039712-36409",
"point": {"x": 0.6753461334176798, "y": 0.49605444348117467},
"type": "marker",
},
{
"children": {},
"code": "ELBOW",
"mid": "20230220170039712-60395",
"point": {"x": 0.6380898632306548, "y": 0.38045402908259107},
"type": "marker",
},
],
"type": "pose",
},
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(list(label.jobs.keys()))
['JOB_0']
print(label.jobs["JOB_0"].annotations[0].category)
{'name': 'HEAD'}
print("Number of points in this annotation: ", len(label.jobs["JOB_0"].annotations[0].points))
Number of points in this annotation: 5
for point in label.jobs["JOB_0"].annotations[0].points:
print(point.code, point.point)
RIGHT_EARBASE {'x': 0.350897302238901, 'y': 0.18537832978498114}
RIGHT_EYE {'x': 0.3581081932428414, 'y': 0.2305347416594279}
NOSE {'x': 0.38815357242592613, 'y': 0.32807259130823285}
LEFT_EYE {'x': 0.4386476019456967, 'y': 0.23889914422760516}
LEFT_EARBASE {'x': 0.46187314422288966, 'y': 0.1875659030559057}
Video jobs
A video label has an additional attribute .frames that returns the annotations for each frame.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"FRAME_CLASSIF_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"OBJECT_A": {"children": [], "name": "Object A"},
"OBJECT_B": {"children": [], "name": "Object B"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Categories",
"isChild": False,
"mlTask": "CLASSIFICATION",
"models": {},
"isVisible": False,
"required": 1,
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"0": {},
"1": {},
"2": {},
"3": {},
"4": {},
"5": {
"FRAME_CLASSIF_JOB": {
"categories": [{"confidence": 100, "name": "OBJECT_A"}],
"isKeyFrame": True,
"annotations": [],
}
},
"6": {
"FRAME_CLASSIF_JOB": {
"categories": [{"confidence": 42, "name": "OBJECT_B"}],
"isKeyFrame": False,
"annotations": [],
}
},
"7": {},
"8": {},
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="VIDEO")
for i, frame_annotations in enumerate(label.jobs["FRAME_CLASSIF_JOB"].frames):
print(f"Frame {i}: {frame_annotations}")
Frame 0: {}
Frame 1: {}
Frame 2: {}
Frame 3: {}
Frame 4: {}
Frame 5: {'isKeyFrame': True, 'categories': [{'name': 'OBJECT_A', 'confidence': 100}], 'annotations': []}
Frame 6: {'isKeyFrame': False, 'categories': [{'name': 'OBJECT_B', 'confidence': 42}], 'annotations': []}
Frame 7: {}
Frame 8: {}
frame = label.jobs["FRAME_CLASSIF_JOB"].frames[5]
print(frame.category.name)
OBJECT_A
The syntax is similar for object detection jobs on video:
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"JOB_0": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"OBJECT_A": {"children": [], "name": "Train", "color": "#733AFB"},
"OBJECT_B": {"children": [], "name": "Car", "color": "#3CD876"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Track objects A and B",
"isChild": False,
"tools": ["rectangle"],
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"models": {"tracking": {}},
"isVisible": True,
"required": 0,
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"0": {},
"1": {
"JOB_0": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
{"x": 0.30, "y": 0.63},
{"x": 0.30, "y": 0.55},
{"x": 0.36, "y": 0.55},
{"x": 0.36, "y": 0.63},
]
}
],
"categories": [{"name": "OBJECT_B"}],
"mid": "20230407140827577-43802",
"type": "rectangle",
"isKeyFrame": True,
}
]
}
},
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="VIDEO")
print(label.jobs["JOB_0"].frames[1].annotations[0].category.name)
OBJECT_B
Named entities recognition jobs
For NER jobs, the content of the job reponse is a list of annotations.
Those annotations can be accessed through the .annotations or .entity_annotations attributes.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"NER_JOB": {
"mlTask": "NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
"content": {
"categories": {"ORG": {}, "PERSON": {}},
"input": "radio",
},
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"NER_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"categories": [{"name": "ORG", "confidence": 42}],
"beginOffset": 21,
"content": "this is the text for Kili",
"mid": "mid_a",
},
{
"categories": [{"name": "PERSON", "confidence": 100}],
"beginOffset": 8,
"content": "this is Toto's text",
"mid": "mid_b",
},
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="TEXT")
print("Number of annotations in this label: ", len(label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations))
Number of annotations in this label: 2
print(label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations == label.jobs["NER_JOB"].entity_annotations)
True
print(label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations[0].category)
{'name': 'ORG', 'confidence': 42}
print(label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations[0].begin_offset)
21
print(label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations[0].content)
this is the text for Kili
print(label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations[0].mid)
mid_a
It is also possible to iterate over the annotations of this label:
for annotation in label.jobs["NER_JOB"].annotations:
print(annotation)
{'categories': [{'name': 'ORG', 'confidence': 42}], 'beginOffset': 21, 'content': 'this is the text for Kili', 'mid': 'mid_a'}
{'categories': [{'name': 'PERSON', 'confidence': 100}], 'beginOffset': 8, 'content': "this is Toto's text", 'mid': 'mid_b'}
Named entities recognition in PDF jobs
For PDF assets, a parsed NER label has a few additional attributes such as .page_number_array and .polys.
The description of those attributes can be found in the documentation.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": [], "color": "#472CED", "name": "A"},
"B": {"children": [], "name": "B", "color": "#5CE7B7"},
"C": {"children": [], "name": "C", "color": "#D33BCE"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Job name",
"mlTask": "NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
}
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"annotations": [
{
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
[
{"x": 0.46269795405629893, "y": 0.26256487006078677},
{"x": 0.46269795405629893, "y": 0.278286415605941},
{"x": 0.602529939052542, "y": 0.26256487006078677},
{"x": 0.602529939052542, "y": 0.278286415605941},
]
]
}
],
"pageNumberArray": [1],
"polys": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
[
{"x": 0.46269795405629893, "y": 0.26256487006078677},
{"x": 0.46269795405629893, "y": 0.278286415605941},
{"x": 0.602529939052542, "y": 0.26256487006078677},
{"x": 0.602529939052542, "y": 0.278286415605941},
]
]
}
],
}
],
"categories": [{"confidence": 100, "name": "C"}],
"content": "Some content",
"mid": "20230502085706687-73004",
},
{
"children": {},
"annotations": [
{
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
[
{"x": 0.18745653985687646, "y": 0.4369143838760365},
{"x": 0.18745653985687646, "y": 0.45263593566837257},
{"x": 0.4306102589135375, "y": 0.4369143838760365},
{"x": 0.4306102589135375, "y": 0.45263593566837257},
]
]
}
],
"pageNumberArray": [1],
"polys": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
[
{"x": 0.18745653985687646, "y": 0.4369143838760365},
{"x": 0.18745653985687646, "y": 0.45263593566837257},
{"x": 0.4306102589135375, "y": 0.4369143838760365},
{"x": 0.4306102589135375, "y": 0.45263593566837257},
]
]
}
],
}
],
"categories": [{"confidence": 100, "name": "A"}],
"content": "chier compressé “Coregist",
"mid": "20230502085709115-90490",
},
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="PDF")
print("Number of annotations: ", len(label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations))
Number of annotations: 2
first_ann = label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations[0]
print(first_ann.content)
Some content
print(first_ann.category)
{'name': 'C', 'confidence': 100}
The NER in PDFs json response format is a bit complex, and thus requires to use the .annotations attribute a second time. You can read more about it in the documentation.
print(first_ann.annotations[0].page_number_array)
[1]
print(first_ann.annotations[0].polys)
[{'normalizedVertices': [[{'x': 0.46269795405629893, 'y': 0.26256487006078677}, {'x': 0.46269795405629893, 'y': 0.278286415605941}, {'x': 0.602529939052542, 'y': 0.26256487006078677}, {'x': 0.602529939052542, 'y': 0.278286415605941}]]}]
print(first_ann.annotations[0].bounding_poly)
[{'normalizedVertices': [[{'x': 0.46269795405629893, 'y': 0.26256487006078677}, {'x': 0.46269795405629893, 'y': 0.278286415605941}, {'x': 0.602529939052542, 'y': 0.26256487006078677}, {'x': 0.602529939052542, 'y': 0.278286415605941}]]}]
Relation jobs
A relation job is a job that links two annotations together. You can read more about it in the documentation.
Named entities relation jobs
A NER relation parsed label has the .start_entities and .end_entities attributes.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"RELATION_1": {
"children": [],
"color": "#472CED",
"name": "Relation 1",
"endEntities": ["B"],
"startEntities": ["A"],
}
},
"input": "radio",
},
"mlTask": "NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
},
"NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": [], "color": "#5CE7B7", "name": "A"},
"B": {"children": [], "name": "B", "color": "#D33BCE"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"mlTask": "NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
},
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"beginId": "main/[0]",
"beginOffset": 159,
"categories": [{"name": "A"}],
"content": "KBDFR",
"endId": "main/[0]",
"endOffset": 164,
"mid": "123",
},
{
"children": {},
"beginId": "main/[0]",
"beginOffset": 145,
"categories": [{"name": "B"}],
"content": "KBDJPN",
"endId": "main/[0]",
"endOffset": 151,
"mid": "456",
},
]
},
"NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"categories": [{"name": "RELATION_1"}],
"endEntities": [{"mid": "456"}],
"mid": "20230502100607943-6453",
"startEntities": [{"mid": "123"}],
}
]
},
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="TEXT")
print(list(label.jobs.keys()))
['NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION_JOB', 'NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB']
print("Annotation content: ", label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations[0].content)
print("Category: ", label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations[0].category.name)
print("Begin offset: ", label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations[0].begin_offset)
print("End offset: ", label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations[0].end_offset)
Annotation content: KBDFR
Category: A
Begin offset: 159
End offset: 164
Here is how to print the unique IDs and names of the entity recognition annotations:
for ann in label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RECOGNITION_JOB"].annotations:
print(ann.mid, ann.category.name)
123 A
456 B
print(label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION_JOB"].annotations[0].category.name)
print(label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION_JOB"].annotations[0].start_entities)
print(label.jobs["NAMED_ENTITIES_RELATION_JOB"].annotations[0].end_entities)
RELATION_1
[{'mid': '123'}]
[{'mid': '456'}]
We can see that the relation annotation above refers to the entity annotations using their unique IDs.
Object detection relation jobs
For object detection relation jobs, the relation data is accessible through the .start_objects and .end_objects attributes.
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": [], "color": "#472CED", "name": "A"},
"B": {"children": [], "name": "B", "color": "#5CE7B7"},
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "BBOX",
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"required": 1,
"tools": ["rectangle"],
"isChild": False,
},
"OBJECT_RELATION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"RELATION_1": {
"children": [],
"color": "#D33BCE",
"name": "Relation 1",
"startObjects": ["A"],
"endObjects": ["B"],
}
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "Relation job",
"mlTask": "OBJECT_RELATION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": False,
},
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
{"x": 0.11634755020512799, "y": 0.49755605764956},
{"x": 0.11634755020512799, "y": 0.22714821030828314},
{"x": 0.4035032060305503, "y": 0.22714821030828314},
{"x": 0.4035032060305503, "y": 0.49755605764956},
]
}
],
"categories": [{"name": "A"}],
"mid": "20230502102127826-44552",
"type": "rectangle",
},
{
"children": {},
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
{"x": 0.539654594568466, "y": 0.8005026086128164},
{"x": 0.539654594568466, "y": 0.5413150038998081},
{"x": 0.7760629146661198, "y": 0.5413150038998081},
{"x": 0.7760629146661198, "y": 0.8005026086128164},
]
}
],
"categories": [{"name": "B"}],
"mid": "20230502102129606-15732",
"type": "rectangle",
},
]
},
"OBJECT_RELATION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {},
"categories": [{"name": "RELATION_1"}],
"endObjects": [{"mid": "20230502102129606-15732"}],
"mid": "20230502102131372-75485",
"startObjects": [{"mid": "20230502102127826-44552"}],
}
]
},
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(list(label.jobs.keys()))
['OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB', 'OBJECT_RELATION_JOB']
for ann in label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations:
print(ann.mid, ann.category.name)
20230502102127826-44552 A
20230502102129606-15732 B
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_RELATION_JOB"].annotations[0].category)
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_RELATION_JOB"].annotations[0].start_objects)
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_RELATION_JOB"].annotations[0].end_objects)
{'name': 'RELATION_1'}
[{'mid': '20230502102127826-44552'}]
[{'mid': '20230502102129606-15732'}]
Child jobs
Use the .children attribute to access nested (child) labels:
json_interface = {
"jobs": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"content": {
"categories": {
"A": {"children": ["TRANSCRIPTION_JOB"], "color": "#472CED", "name": "A"}
},
"input": "radio",
},
"instruction": "BBox job",
"mlTask": "OBJECT_DETECTION",
"required": 1,
"tools": ["rectangle"],
"isChild": False,
},
"TRANSCRIPTION_JOB": {
"content": {"input": "textField"},
"instruction": "Transcription",
"mlTask": "TRANSCRIPTION",
"required": 1,
"isChild": True,
},
}
}
dict_label = {
"jsonResponse": {
"OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB": {
"annotations": [
{
"children": {
"TRANSCRIPTION_JOB": {"text": "This is a transcription of a bbox"}
},
"boundingPoly": [
{
"normalizedVertices": [
{"x": 0.23517058020185444, "y": 0.40330601957210255},
{"x": 0.23517058020185444, "y": 0.22939225883393688},
{"x": 0.4468241023835235, "y": 0.22939225883393688},
{"x": 0.4468241023835235, "y": 0.40330601957210255},
]
}
],
"categories": [{"name": "A"}],
"mid": "20230502102626089-88764",
"type": "rectangle",
}
]
}
}
}
label = ParsedLabel(dict_label, json_interface=json_interface, input_type="IMAGE")
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].type)
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].category.name)
rectangle
A
print(label.jobs["OBJECT_DETECTION_JOB"].annotations[0].children["TRANSCRIPTION_JOB"].text)
This is a transcription of a bbox